Symptoms Of Zinc Deficiency In Neonates
Getting too much zinc on a regular basis may cause low copper levels in the body a reduced immunity and low levels of the good cholesterol. Failure to evaluate and manage biotinidase deficiency at an early stage can cause irreversible neurodevelopmental abnormalities and can lead to developmental delay and autistic behavior.
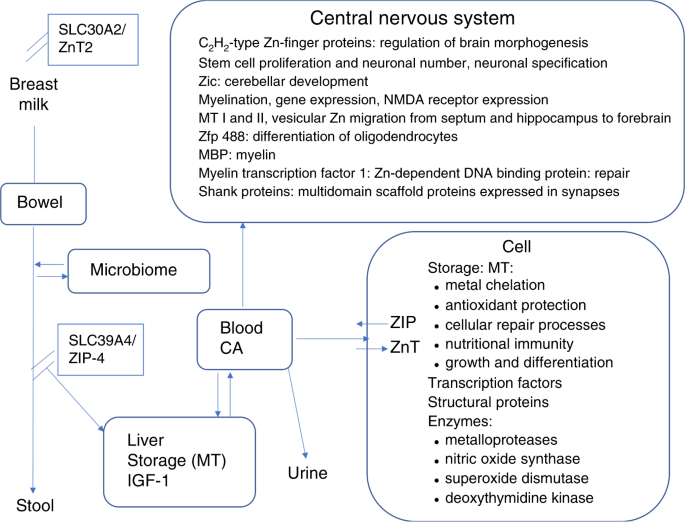
Role Of Zinc In Neonatal Growth And Brain Growth Review And Scoping Review Pediatric Research
Deficiencies can occur because of poor dietary intake long-term parenteral nutrition without supplementation and enteral causes such as malabsorption.

Symptoms of zinc deficiency in neonates. Diminished food intake usually due to reduced ability to taste and smell. It is possible for children to get too much zinc. Growth deficits manifest as lower weight length and head circumference as well as changes in body composition.
Diarrhea is one of the frequently and early occurred symptoms in zinc deficiency as well as worsens the zinc-deficiency state by losing endogenous zinc. Zinc deficiency may adversely affect the fetal brain function and cognitive development amongst neonates and infants neuropsychological performance in children and cognitive function in the elderly. Symptoms of the zinc deficiency also oc- curred in these patients during the anabolic phase suggesting that tissue demand for zinc may be increased at that time Therefore zinc should be in- cluded on a regular basis in all parenteral nutritional solutions in amounts sufficient to meet estimated needs for growth and tissue repair.
1 Loss into digestive fluid. Serum zinc. Toxic Elements The most important of these is Fluorine.
The most common signs of zinc deficiency disorder include dermatitis and growth impairment which can be attributed to multiple causes. Growth failure in the presence of adequate energy and protein intake. 25 to 40 weeks with zinc deficiency dermatitis who developed erosive impetiginized periorificial dermatitis at 10 weeks of age corresponding to a mean gestational age of 414 weeks with a range of 3644 weeks but who were otherwise well.
When neonates diagnosed by neonatal screening receive biotin they develop normally without having any symptoms and those with symptoms respond quickly to biotin treatment. Acrodermatitis enteropathica is characterized by intermittent simultaneous occurrence of diarrhea and dermatitis with failure to thrive. These deficits precede the development of BPD and persist post-discharge.
Early occurred symptoms in zinc deficiency as well as worsens the zinc-deficiency state by losing en-dogenous zinc. Furthermore compared to infants without BPD those with BPD have increased resting metabolic rates and energy expenditure. Your brain needs zinc too.
We report ten infants mean gestational age. In the latter condition the effects of zinc therapy are dramatic and potentially lifesaving. Zinc is also important for normal growth and development of children both with and without diarrhoea 2426.
It presents with the classic triad of. This paper reviews the features of mild-to-moderate zinc deficiency which include growth faltering deficits in immune function and altered integrity and function of. Zinc deficiency is closely associated with stunting respiratory infections diarrhea and dermatitis.
The skin lesions have a character-istic distribution of primarily localizing in the ex-tremities and adjacent to the body orifices. Zinc deficiency can occur in infants and children as a result of inadequate dietary zinc intake disturbed zinc metabolism secondary to numerous disease states and an inherited defect in zinc metabolism in acrodermatitis enteropathica. In Japan zinc acetate dihydrate has been approved as a therapeutic agent for hypozincemia and is also administered to neonates and.
It may also cause an altered smell sensation. Zinc deficiency causes a chronic dry scaly cracked skin non-inflammatory in nature and although well recognized in Europe is uncommon in the tropics. Cutaneous symptoms were initially misdiagnosed as eczema or impetigo in 810 80.
Acrodermatitis enteropathica is a rare disorder associated with zinc deficiency. Zinc deficiency is associated with an increased risk of gastrointestinal infections adverse effects on the structure and function of the gastrointestinal tract. Most commonly the rashes are erythematous ves-iculobullous and pustular.
Three premature infants with zinc deficiency who had an unusual presentation with generalized edema and hypoproteinemia between 5 and 9 weeks of age are described. Peri- acral and periorificial dermatitis. Alopecia of the scalp eyebrows and eyelashes is a usual feature.
Because it is involved in so many processes clinical features of zinc deficiency are non-specific and include the development of eye and skin lesions growth retardation alopecia and diarrhea. Primary acrodermatitis enteropathica is due to an inherited zinc transporter defect resulting in. Symptoms of a zinc overdose include loss of appetite nausea vomiting stomach cramps diarrhea and headaches.
While 86 of total body zinc is stored in skeletal muscle and bone only 01 is found in plasma 4 which is kept at a tightly regulated concentration of 1218 mcmolL. Zinc deficiency in neonates and infants is associated with dermatitis growth failure infection and autism spectrum disorde r4 5. Signs of Zinc Deficiency.
Zinc deficiency is estimated to contribute to over half a million deaths per year in infants and children under 5 years of age. Zinc deficiency disorderassociated dermatitis which is a physical manifestation is present in only the most severe cases. Foods poor in animal protein vegetarians Child intractable diarrhea intestinal fistula 2 Loss of zinc during food processing gastrointestinal disease associated with diarrhea desalting during production.
The infants were fed their own mothers milk supplemented with a proprietary formula after the first 2 to 3 weeks of life. The skin lesions have a characteristic distribution of primarily localizing in the extremities and adjacent to the body orifices. The skin lesions are bullous.

Recommendations For Zinc In Neonates By Enteral Or Parenteral Route Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Zinc Supplementation In Preterm Neonates And Neurological Development A Randomized Controlled Trial
Pdf Serum Zinc Level And Prognosis Of Neonatal Sepsis
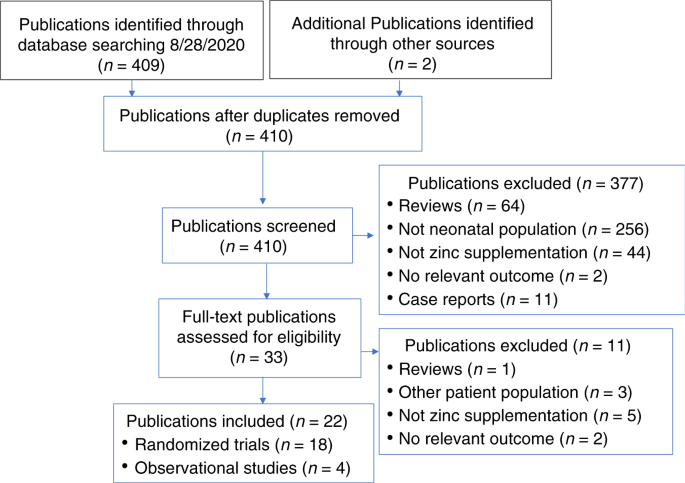
Role Of Zinc In Neonatal Growth And Brain Growth Review And Scoping Review Pediatric Research
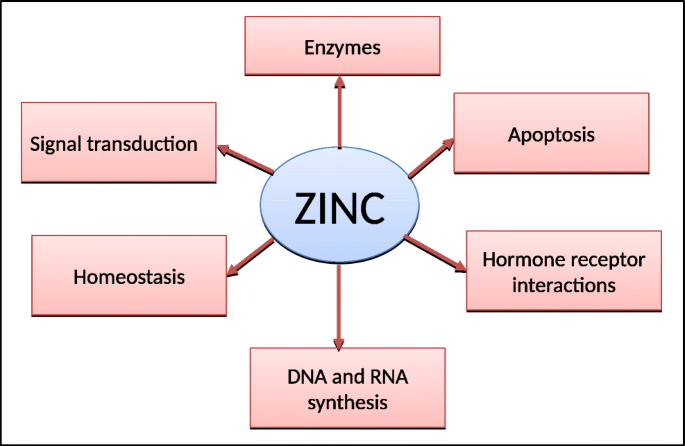
Role Of Zinc In Neonatal Sepsis Springerlink
Posting Komentar untuk "Symptoms Of Zinc Deficiency In Neonates"